
Cloud Computing Platform on Autopilot
Built by Developers for Developers!
curl https://get.tau.link/tau | sh
tau config generate -n mycould.xyz -s compute --ip A.B.C.D --dv --swarm
tau start -s compute
Deploy on your own hardware
And on your favorite Cloud Platform and bare-metal provider!
Embrace Edge-Native
At Taubyte, we're pioneering the Edge-native cloud paradigm. Our autonomous cloud technology intelligently routes requests, optimizes asset caching, and ensures unparalleled user experiences. Experience the pinnacle of cloud innovation with Taubyte, where every interaction is optimized for the Edge, bringing you closer to your users than ever before.
- Horizontal Scaling
-
Forming an overlay mesh network and leveraging distributed protocols like DHTs and CRDTs, these platforms effortlessly extend across diverse hardware and operating systems. This approach ensures unmatched scalability and resilience, guaranteeing efficient performance and reliability on a global scale.
- Caching & Computing
-
Utilizing block exchange with peers, hash addressing, and deduplication, our system offers robust caching capabilities at the edge. Enhanced by WebAssembly, our serverless functions spawn in milliseconds, achieving near-zero cold start times for optimal performance.
Git: The Definitive Source of Truth
Bid farewell to the cumbersome and opaque infrastructure API calls. Taubyte revolutionizes cloud building with Git at its core, ensuring a transparent, auditable, and streamlined process.
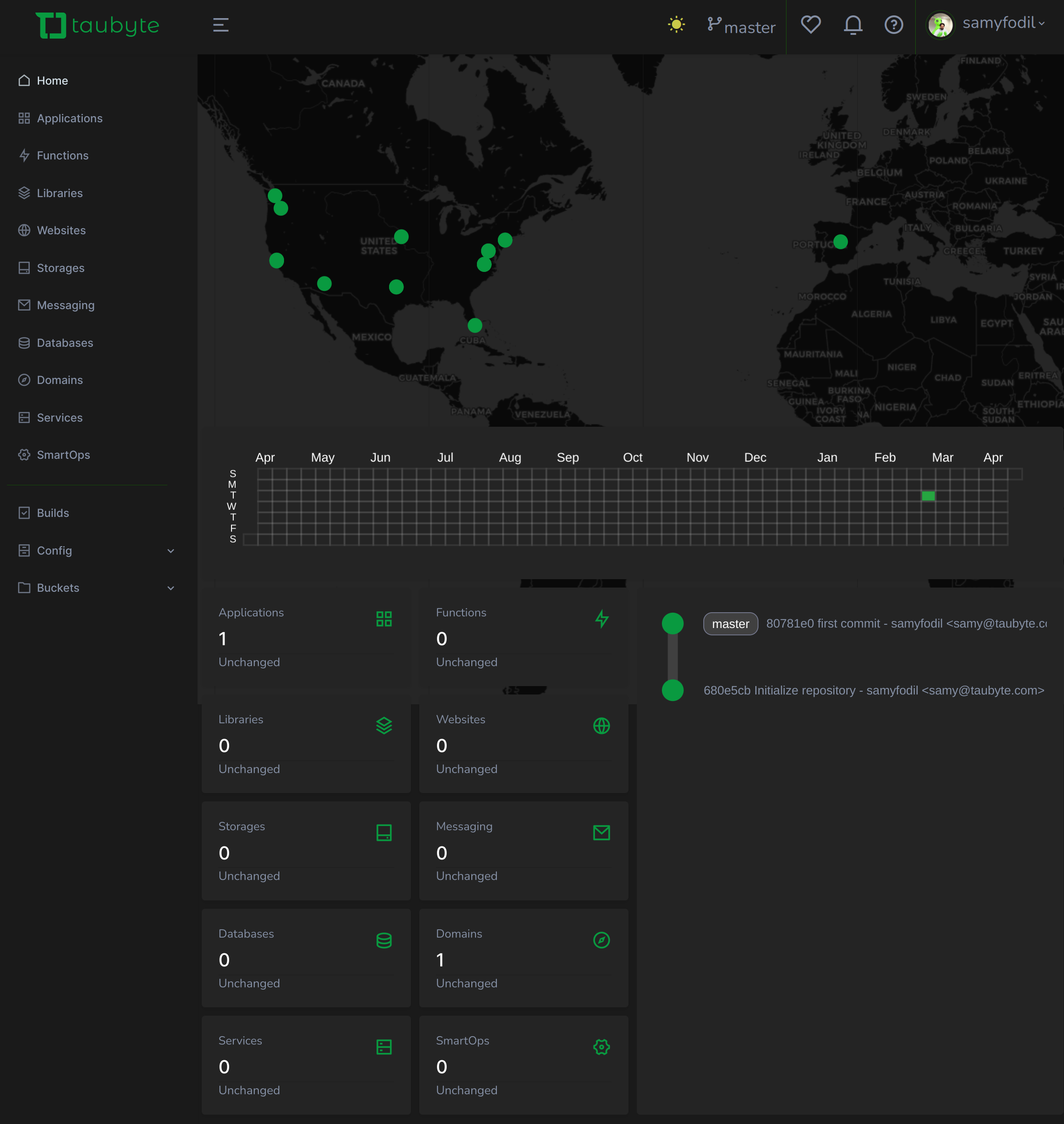
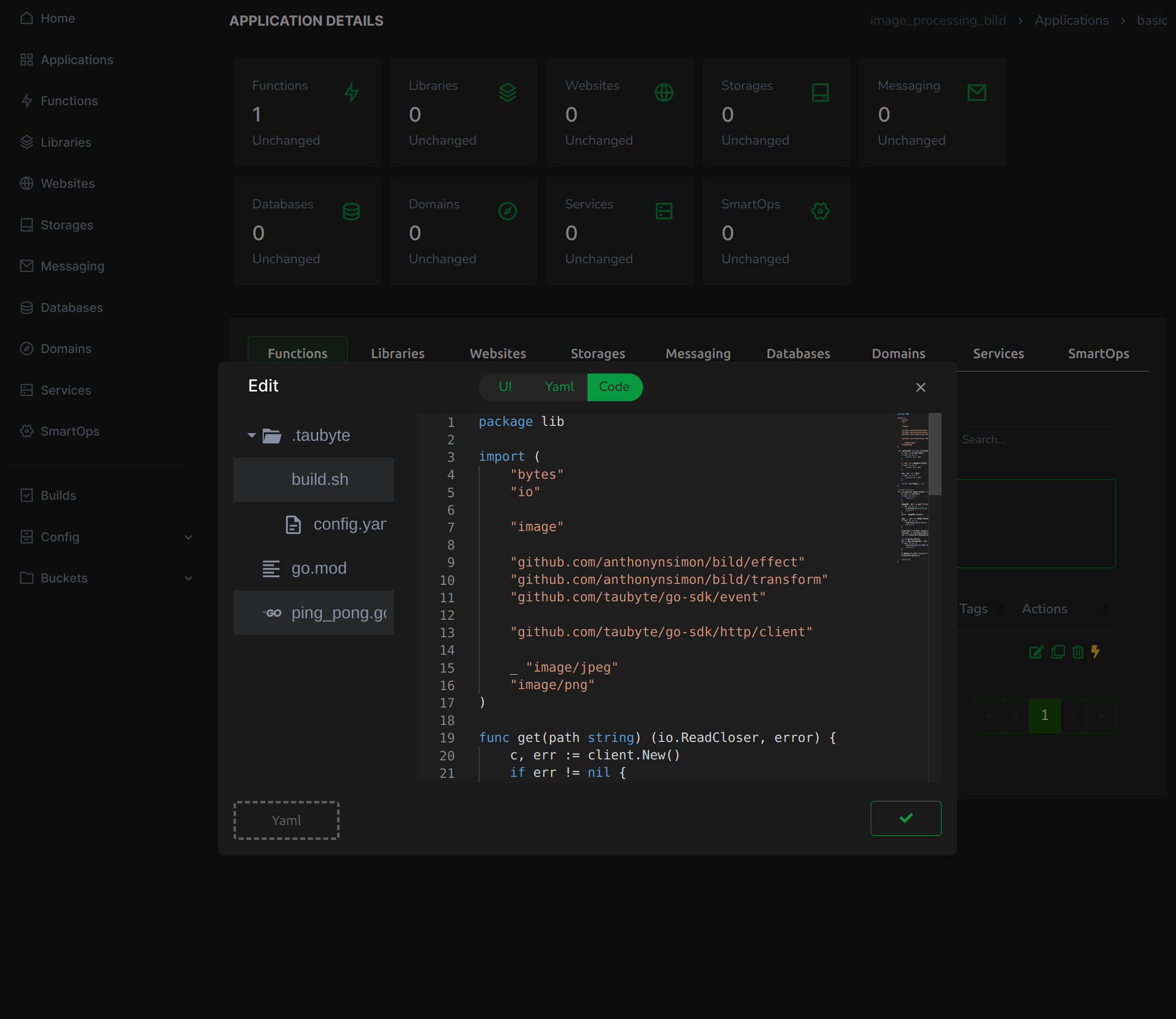
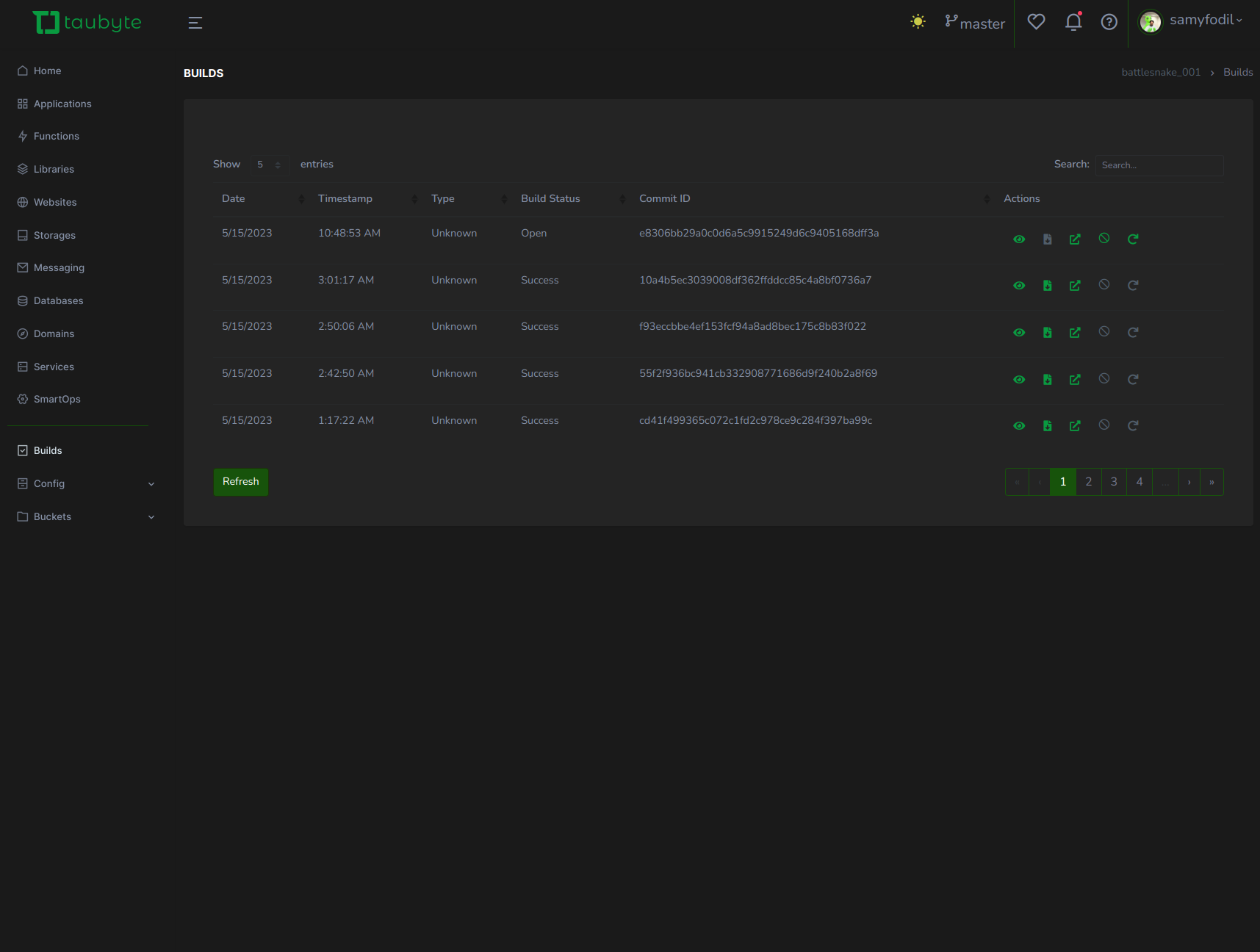
Web Console
Tailored for ease and customization, our Web Console is not just a UI alternative; it's a leap forward. It offers a user-friendly experience that will help you outshine the likes of Fastly, Cloudflare, Netlify, and Vercel. With Taubyte, you get the best of both worlds: the robustness of GitOps and the simplicity of a customizable web interface. This dual approach caters to the diverse needs of software developers, ensuring a smoother, more efficient cloud computing experience.
Try it Customize itElegant CLI
For users who thrive in the shell environment, the tau command line is a delight. It's user-friendly, seamlessly scriptable, and effortlessly integrates into any Go-based automation project, enhancing the overall user experience.
Github Documentation # install with npm
npm i @taubyte/tau
# or self extracting script
curl get.tau.link/cli | sh
# create a project
tau new project -n hello-world
# create a function
tau new function --lang Go|Rust --template ping_pong
# deploy
tau push project
Dreamland - Seamless Local Development
Dreamland empowers developers to effortlessly create a comprehensive cloud environment locally or in a devcontainer, ensuring a reliable and confident development process. Additionally, with libdream, they can construct thorough end-to-end tests, guaranteeing seamless functionality upon deployment.
npm i @taubyte/dream
dream new multiverse
npm i @taubyte/dream
dream new multiverse
Unmatched Developer Experience
Clouds crafted using Taubyte technology redefine the developer experience by providing a comprehensive suite of tools. Central to this is its core Git interface, complemented by powerful abstractions. These features empower developers to rapidly create remarkable, planet-scale applications with ease and efficiency.


WebAssembly Serverless Function to Generate Avatars

Build an Edge-Native URL Shortener
